Are all electric cars automatic?
It is assumed that all electric cars would be automatic and that is a correct assumption… for the most part. Most electric cars are automatic because EVs are powered by an electric motor, which means the speed and power of an electric car remain constant, and therefore doesn’t require a change of gears. More first-time drivers are now actually skipping the manual driving test and opting for an automatic licence because electric cars are set to be the future of driving - see our blog about what will happen to petrol cars after 2035 to learn about the future of driving. Manufacturers like Toyota and Ford have created cars with manual transmissions (gears) and clutches unique, like the Ford Mustang model, but these are one-off examples that are unlikely to ever hit the roads.
There are many different types of car transmissions on the market, including manual, automatic, continuously variable, semi-automatic, and dual-clutch transmissions. In this post, we will unearth what these different types of transmissions are, whether they relate to electric cars and the benefits they offer.
This image is sourced from Auto Design Magazine
Transmission Systems in Electric Vehicles
The transmission of power from the engine to the wheels is a crucial aspect of a car, making the car transmission system vital. Two main types of transmissions, manual and automatic, play key roles. However, when it comes to automatic transmissions, there are various types, such as Continuously variable, Semi-automatic, Tiptronic, and dual-clutch transmissions. This diversity is not only relevant to traditional vehicles but also to electric cars, where the electric car's automatic transmission is a noteworthy component. These distinctions are essential for understanding the nuances of how power is efficiently transferred in both conventional and electric vehicles.
The Automatic Misconception
In conventional petrol and diesel vehicles, power from the engine to the wheels is transferred through multi-speed transmissions using gears. Gear shifts are crucial to ensure that the wheels receive the appropriate amount of energy as the engine operates at different RPMs (revolutions per minute). The automatic transmission system detects changes in engine speed and autonomously shifts gears, optimising the energy distribution to the wheels.
However, electric cars have revolutionised this process. Unlike traditional vehicles, electric cars generate a constant amount of torque across a range of RPMs. This inherent characteristic simplifies the mechanism, allowing the electric motor to directly distribute power to the wheels without the need for multi-speed transmissions or subsequent gear shifts. In the realm of electric vehicles (EVs), the elimination of this complexity contributes to a more straightforward and efficient power transfer system.
That being said, not all electric cars are automatic - there are some EVs that require manual transmission (as mentioned previously). This is not necessary because electric cars have no engine, no drive shaft and no gears. Toyota created an electric car prototype that mimics driving a manual transmission, this has been done to preserve the driving experience for car enthusiasts. They also included a floor-mounted speaker to blast fake engine noises, it will also stall if you fumble on the controls to give drivers the full manual experience.
While it's a common belief that all electric cars are automatic, there are exceptions, and some electric vehicles (EVs) come with a manual transmission, as mentioned earlier. This might seem counterintuitive, given that electric cars lack traditional components like an engine, drive shaft, and gears.
Nevertheless, Toyota has challenged this notion by developing an electric car prototype that emulates the feel of driving a manual transmission. This unconventional approach is aimed at preserving the driving experience cherished by car enthusiasts.
This image is sourced from motor1.com
To enhance the illusion, they even incorporated a floor-mounted speaker to simulate engine noises. Interestingly, the prototype will stall if the driver fumbles on the controls, providing a complete manual experience for enthusiasts. Other manufacturers have followed suit, like the Ford Mustang, Jeep Magneto and Lexus all creating cars which have a manual transmission. As the Verge points out, this speaks to a “deep-seated anxiety in the auto industry about the approaching obsolescence of the internal combustion engine.”
Types of Transmissions in EVs
Electric cars come equipped with various types of transmissions, and the specific transmission largely hinges on the type of electric vehicle (EV) you own. If your EV is designed for high speeds, such as sports cars, or if it's a long-range electric vehicle, it may be equipped with a multi-speed transmission. However, this is not hugely common. In this segment, we will explore the specifics of the diverse transmissions found in electric vehicles, shedding light on the distinctions that cater to different performance requirements.
Single-speed transmissions
The majority of electric vehicles (EVs) available today are equipped with a single-speed transmission. This type of transmission efficiently distributes the motor's output speed and torque to the wheels of the vehicle. When the driver activates the accelerator, electric power promptly flows from the vehicle's battery to the motor. The single-speed transmission plays a crucial role in regulating the allocation of power to the wheels, facilitating the movement of the vehicle in either forward or reverse, depending on the selected transmission mode, be it drive or reverse.
Continuously variable transmission
Continuously Variable Transmissions, abbreviated as CVT, are frequently utilized in conventional hybrids and occasionally in plug-in hybrid electric cars. Hybrid vehicles integrate CVT with the electric motor, which provides support to the petrol or diesel engine during acceleration or operates independently at lower speeds. Simultaneously, the CVT adjusts the gear ratio to deliver precisely the required amount of torque, optimizing the overall performance of the hybrid system.
Multi-speed transmission
As previously mentioned, the majority of electric vehicles (EVs) do not incorporate multi-speed transmissions, diverging from the traditional design of petrol and diesel cars. In an electric car, the absence of an engine is compensated by the presence of an electric motor. Unlike internal combustion engines, electric motors can consistently generate a steady amount of torque across a specific range of revolutions per minute (RPM). This characteristic eliminates the need for multiple gears with varied ratios to manage power output. Instead, car manufacturers engineer precise gear ratios to optimise efficiency for the electric motor, alleviating the need for shifting gears in the electric vehicle transmission system. Examples of multi-speed transmissions are in Porsche and Tesla.
This is the Porsche 356 EV by Electrogenic - combining modern electric power with a traditional manual gearbox. The 356 was the first Porsche produced. This car has been converted to an EV by Electrogenic, an Oxford-based company that transforms cars pre-1990 into an EV.
This image is sourced from TopGear
In-wheel transmission
The in-wheel motor serves as a distinctive electric vehicle (EV) drive system, positioning motors directly around each of the driving wheels to provide direct power. This configuration enhances accelerator responsiveness, allowing the car to be finely attuned to the driver's commands. The independent control of the right and left wheels further refines the steering response, enabling the vehicle to move precisely as directed by the driver. Consequently, the in-wheel motor design not only boosts overall performance but also promotes a heightened sense of control and responsiveness, aligning the car more closely with the driver's intentions.
Electric car transmissions vs Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Transmissions
Electric motors are substantially more efficient than internal combustion engines (petrol and diesel) - electric motors can convert over 85% of electrical energy into mechanical energy compared to less than 40% for a gas engine. Most electric motors can operate beyond 10,000 RPM with ease compared to the 6,000 RPM average of many ICE vehicles. A multi-speed transmission, so common to ICE transmissions, causes added weight and extra production costs. Overall, single transmissions can power a car faster than multi-transmissions and this is why electric cars should be considered the superior choice when compared with diesel or petrol counterparts. This difference in transmission also makes the driving experience easier, so many people now are prioritising an automatic driving test over a manual because they know electric cars are the future - this, in theory, should speed up the amount of time it takes someone to pass their test. After all, they do not then have to learn how to use gears which can be a big hurdle for many when learning to drive.
EVs are faster and easier to drive as a result of single-speed transmissions, it’s a win-win.
Future trends and innovations for electric car transmissions
Electric vehicle technology is constantly improving and therefore, electric car transmissions will evolve as more people swap their petrol cars for electric. There are many requirements for the transmissions in EVs such as noise reduction, increased efficiency, compact designs and designs that can handle high torque.
Spiral Bevel Gears
These gears use helical teeth (they are cut at an angle to the hole rather than straight) which produce less noise and fewer vibrations. This reduces stress and fatigue put onto the gears, improving their durability and performance and subsequently reducing the cost of repairs over the years. We may expect to see these used more frequently when manufacturing EVs
Improved transmission fluid
Transmission fluids play a crucial role in ensuring efficient lubrication, especially in the presence of contaminants like dust, facilitating the seamless movement of transmission components. This enhanced lubrication not only leads to better performance but also contributes to the prolonged durability of the transmission system. Continuous innovation is evident in the development of new fluid formulas, with rigorous testing conducted to ensure optimal effectiveness. Among the products available on the market, Shell's EV-Plus E-Transmission Fluid stands out. Leveraging cutting-edge technology, this fluid surpasses the latest requirements for electric vehicle (EV) transmissions, underscoring the commitment to advancing transmission fluid capabilities in line with evolving industry needs.
Hybrid vehicle gear transmission
For hybrid vehicles, an important area of innovation lies in the automatic gearbox. Beyond its role in conventional gear shifts, the hybrid gearbox seamlessly transitions between hybrid and electric modes, responding to factors such as the battery's charge level and the driver's accelerator input. Enhancing this process through advancements in transmissions is poised to significantly elevate the overall driving experience of hybrid vehicles. By refining the interaction between gears and power modes, innovations in this key aspect promise to optimise performance and responsiveness, contributing to a more efficient and enjoyable driving experience for hybrid vehicle enthusiasts.
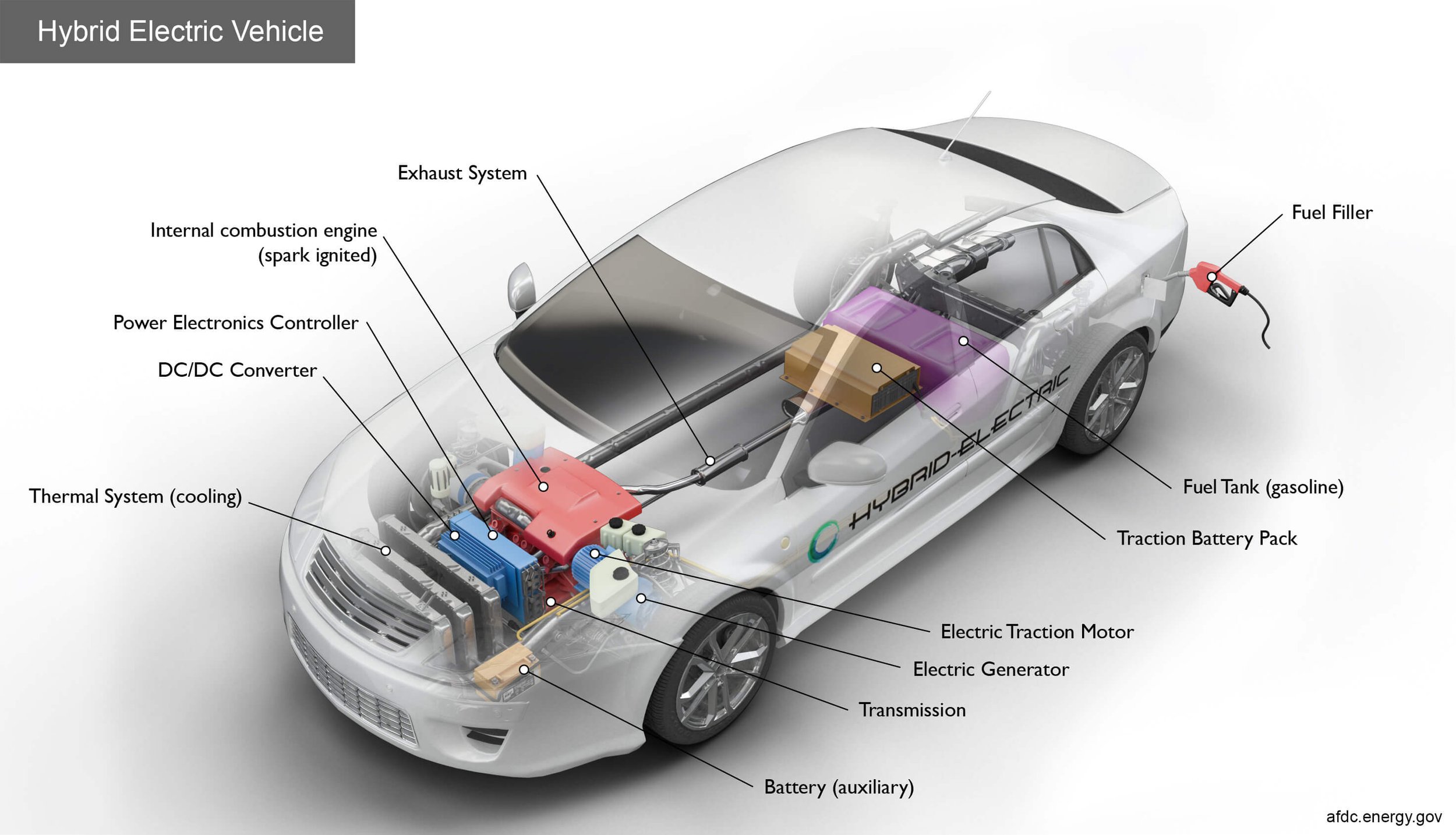
The diagram shows the components of a hybrid electric vehicle from the electric generator to the fuel tank. In case you didn’t know, a hybrid electric vehicle can't be plugged in to charge the battery. Instead, the battery is charged through regenerative braking and by the internal combustion engine.
This image is sourced from the US Department of Energy
Exploring the assumption that all cars are automated, we find that while most EVs are automatic due to generating consistent torque across RPMs, exceptions like Toyota's manual prototype challenge this norm, preserving manual driving.
The article covers various EV transmission systems: single-speed, continuously variable, multi-speed, and in-wheel. It contrasts electric car transmissions with ICE counterparts, emphasizing the efficiency of single-speed transmissions.
The future is very exciting because we are seeing innovations like spiral bevel gears, improved transmission fluid, and advancements in hybrid vehicle gear transmissions. These developments indicate an evolving landscape in response to growing EV adoption.
Want to learn more about what we do at The Electric Car Scheme?
We make it easy for employees to unlock government tax incentives and save 20-50% on any electric car. It’s similar to the Cycle to Work Scheme, only for EVs! You can learn more about how it works for employees and companies by visiting our website and having a browse.
Images on this site are sourced from third party websites as listed below each image and are the property of their respective owners. If you believe any content infringes your copyright, please contact us at marketing@electriccarscheme.com.